Linux commands
BASIC
COMMANDS
Hostname-
hostname command in Linux is used to obtain the DNS(Domain Name System) name
and set the system’s hostname or NIS(Network Information System) domain name.
Hostname-A
: This option is used to get all FQDNs(Fully Qualified Domain Name) of the host
system.
Hostname
-b : Used to always set a hostname. Default name is used if none specified
Hostname
-d : This option is used to get the Domain if local domains are set
Hostname
-f : This option is used to get the Fully Qualified Domain Name(FQDN). It
contains short hostname and DNS domain name.
Hostname
-i option:This option is used to get the IP(network) addresses
Hostname
-V : gives version number as output

Uname
command
Uname
command is used to display basic information about the operating system and
hardware. With options, Uname prints kernel details, and system architecture.
Uname
-s kernal name
Uname
-r kernal release
Uname
-v kernal version
Uname
-n node name
Uname
-m hardware name
Uname
-I hardware platform
Uname-p
processor type
Uname-a
shows all parameters
Date
commands
date
command is used to display the system date and time. date command is also used
to set date and time of the system
Date
-u display time in GMT
Date
--date=" string " Displays the
given date string in the format of date
Using –date option for displaying past
dates:
$date --date="2 year ago"$date --date="next tue"$date +%[format-option]-Format specifiers used with date command:
$date +% d
$date +% m
Cal command calcommand is a calendar command in Linux which is used to see the calendar of a specific month or a whole year.
cal [ [ month ] year] PWD command
The pwd command stands for print working
directory. It is one of the most basic and frequently used commands in Linux. When
invoked the command prints the complete path of the current working directory.
Mkdir command
mkdir command in Linux allows the user to
create directories
This
command can create multiple directories at once as well as set the permissions
for the directories.
Mkdir
-p
-p: A
flag which enables the command to create parent directories as necessary. If
the directories exist, no error is specified.
-m: This
option is used to set the file modes, i.e. permissions, etc. for the created
directories
Cd command
cd command in linux known
as change directory command. It is used to change current working directory
cd /: this command is used to change directory to the
root directory, The root directory is the first directory in your filesystem
hierarchy.
cd dir_1/dir_2/dir_3: This
command is used to move inside a directory from a directory
cd ~ : this
command is used to change directory to the home directory
cd .. : this
command is used to move to the parent directory of current directory, or the
directory one level up from the current directory. “..” represents parent
directory.
FILE
create commands
Touch
The
touch command allows us to update the timestamps on existing files and
directories as well as creating new, empty files.
Cat
The
cat command is mainly used to read and concatenate files, but it can also be
used for creating new files.
Vi-
virtual editor vi filename.txt command used to create virtual editor
By
pressing keys in keyboard to perform action in vi
Insert
- a,I,o,u
- :w - Save the file but keep it open
- :q - Quit without saving
- :wq - Save the file and quit
DU
-disk usage command
Command du stands for Disk Usage.
It is used to check the information of disk usage of files and directories on a
system.
du -a List all files and directories size
du -h Display in human readable format
du -c Display grand total in the output
du -s Display only total
DF
command
Linux df command is used to
display the disk space used in the file system. The 'df'
stands for "disk filesystem." It defines the
number of blocks used, the number of blocks available, and the directory where
the file system is mounted.
Df -To display the disk space
usage, execute the df command without any argument.
Df -h -Display the disk space
usage in a human-readable form
Df -T -display file system
type
Df -t filename -display
specific file system type
TOP
command
top
command is used to show the Linux processes. It provides a dynamic real-time
view of the running system. Usually, this command shows the summary information
of the system and the list of processes or threads which are currently managed
by the Linux Kernel.
CPU
information commands
Using
cat command to get cpu information
Cat/proc/cpuinfo
The command lscpu prints
CPU architecture information from sysfs and /proc/cpuinfo as
shown below:
Memory
information commands
Cat
/proc/meminfo
This is a virtual file that reports the
amount of available and used memory. It contains real-time information about
the system’s memory usage as well as the buffers and shared memory used by the
kernel
free Command to Display
the Amount of Physical and Swap Memory
The vmstat command is a
useful tool that reports virtual memory statistics.
WHO command
who is a command-line utility that prints a list of
currently logged in users. It can also show the current run level, time of the
last system boot, and more.
LS commands
ls with no option list files and directories in
bare format where we won’t be able to view details like file types, size,
modified date and time, permission and links etc.
ls -l (-l is character not
one) shows file or directory, size, modified date and time, file or folder name
and owner of file and its permission.
Ls
-a list all files including hidden files
Ls-
lh list all files with human readable formet
Ls
-ltr With combination of -ltr will shows latest
modification file or directory date as last.
Cp command
cp stands
for copy. This command is used to copy files or group of
files or directory. It creates an exact image of a file on a disk with
different file name. cp command require at least two
filenames in its arguments
MV command
mv stands
for move. mv is used to move one or more files or
directories from one place to another in a file system
RM command
rm stands for remove here. rm
command is used to remove objects such as files, directories, symbolic links
and so on from the file
HEAD command
The head command, as the name implies, print the top N
number of data of the given input by default it prints top 10 lines
Tail command
The tail command, as the name implies, print the last N
number of data of the given input. By default it prints the last 10 lines of
the specified files.
Word count commands
Wc -l counting number of lines in the file
Wc -w counting words
Wc -c counting characters
ROOT commands
On every Linux system, the root account is a special user
with administrative rights. Logging in as root (or executing commands with root
privileges) is necessary for many tasks.
There is a special command named su (for "super
user," or "switch user") that allows you to run commands as the
root account temporarily.
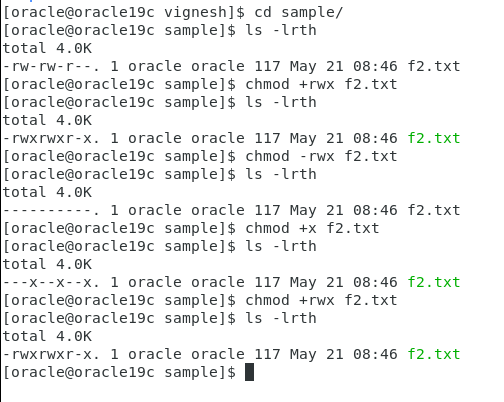
Permission commands
chmod +rwx filename to add permissions.
chmod -rwx directoryname to remove permissions.
chmod +x filename to allow executable permissions.
chmod -wx filename to take out write and executable
permissions.
File Compress commands
To reduce the file size by using compress commands
gzip - command used to compress the file size
Gunzip - unzip the original file size