SQL COMMANDS
TABLE CREATION
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE table_name(column_name1
data_type,column_name2 datatype);
Example:
Employee database
Table creation
Create table name as an employee with
five columns employee id, name, address, phone number, blood group.
View table structure.
DESC:
Using the desc command we can view the overall table structure. It displays column names and datatypes.
Desc employee;
Add column into table:
Using
alter command we can add more column in table
Example:
In
employee table already we create with five columns and we can add one more
column.
We
add department column in employee table using alter command.
Remove one column:
In
alter table command we can remove one column also possible.
In
employee table blood group no need so we can remove it
Using
drop command we remove blood group
Change column datatype:
Using
alter command we change column datatype by use modify command
In
employee table we change phone number datatype
Previously
phone number datatype as number now it can be changed as varchar2
Rename column:
Incase
of any mistake wrongly mention the column name we can rename the column name
Above For example we rename the column department as designation;
Table rename:
We
can rename table name using rename command
Employee
table renamed by employee details.
Create new table:
Create
new table as employee salary
Create new table employee salary with three
columns id,name and salary.
INSERT RECORD INTO TABLE;
There are three possible ways to insert records into database table
*directly
insert values into table
*using
& symbol to add multiple records
*specify
column name add insert values
1.directly insert values into table
In employee table we can directly
add employee id name and salary by using insert command
2.using & symbol to add multiple records
Using
& symbol we add more records in employee salary table
3.specify column name add insert
values
We
specify the column name and add values to the table
Change column values using update command
Employee
salary employee name we add different types of employee names update all name
as single name,
Change single row value using update command
Update single row values by using where
condition specify the row and update the values.
Employee
id 101 salary can be updated.
Grant permission;

We give access our table to other user by
using grant command
Revoke permissions;
We
get back all permission to other users.
Views - desc
Desc user constraints;
Desc - user column level constrains
Retrieve records;
Select
command is used to retrieve records from table
* using all columns retrieval
Select
needed column by specify column name to retrieve records
Retrieve
individual row by using where condition.
COMMIT,ROLLBACK,SAVEPOINT
Save point;
Insert
multiple records in table once we commit all data can be save we give rollback
command only one step undo operation will perform.
Save
point used to create more point in commands
Create
savepoint with name use the name to give rollback command to go that point.
Syntax
Savepoit savepoint_name;
Savepoint p1;
Rollback;
Roll
back moves the specified point one we reach that previous point cannot be worked
only this command moves forward.
First point p1 only rollback complete
p2 cannot performed.
Commit;
Commit
command used to save sql commands. Table we can create multiple records finally
we give commit to save all records.
We
dont give commit command once we close connection they will not saved
SQL CONSTRAINTS
Not null constraints
Column level
Create column not null constraint in
s-id column
Alter
level
To
alter column constraint with alter command
Insert record in not null The
record cannot be accept empty values
Primary key
Table
level
Specifies
the column or columns that uniquely identify a row in the table. NULL values
are not allowed.
Create primary key on sid table
level
Column
level
Foreign key
Table
level
Foreign key is used to relate two
tables it referenced by primary key
Primary
key table
Foreign
key table
Column
level
Using alter command add foreign key constraint in column
level
Unique constraint:
It can be null not
unique
Table
level
Column level using alter method
Default constraint:
Column level
Default key is used to set a default value for column
The given table
trichy mention as default city so add city column in database it can empty take
it as trichy
Alter level
Alter
the column default value.
SQL functions
Functions are used to perform task
in sql we can use built in functions
It has been two type
1.single
row function
2.multi
row function
1.Single row functions:
*String
functions
*Numeric
functions
*Date
function
*Convert
function
*Case
function
*Decode
function
*Null
function
String function
Case-
Uppercase,
Lower case, Initcap
Uppercase
Change
the table column value lower case to upper case
Lower case
Change
column value as lowercase
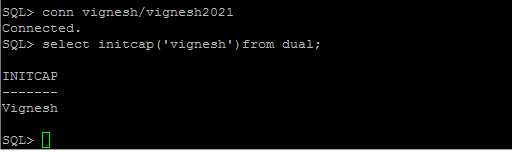
Initcap
Set
letter starting value as capital
Character function
Length,
Replace, Translate, Trim, Ltrim, Rtrim, Lpad, Rpad, Instr, Substr
Length
To
get string character length
Replace
Replace
the old character with new character
Translate
Pass
the two argument third argument as translate value
LTRIM
& RTRIM function
The ltrim function removes the specified
character in left side of the string
The rtrim function check right side of
string if specified character does not exist it return same value otherwise it
remove the value
LPAD
& RPAD functions
The LPAD
function left pads a string with another string to a certain length.
To specify the name and length and
padding symbol
The RPAD
function pads a string with another string in right side of the character
INSTR
& SUBSTR Function
Instr- it returns position of specified
string
substr-The substr functions return a portion of character
Numeric Function
Round
-round the given numeric value
Trunc
- round off the value with specified digit
Power
- power the given value
Sqrt
- square root of the number
Mod
- display the mod remainder value
Abs
- positive number
Ceil
- round the value to next numeric value
Floor
- round the previous numeric value
Date function
Sysdate
- system current date
Month between - specify month between the value
Next
day - next day of specified date
Last
day - previous day of specified date
Add
month - add month to the given date
Convert functions
To_char-
convert date into character
to
_number- convert given number based on digit values
To_date
- covert given date with needed formet
Case function
Case function like as conditional function like if then else statement
check the condition if it true the blook executed otherwise it moves another
block finally else part executed
Multi row functions
●
Aggregate
function
●
Order
by
●
Group
by
●
Having
clause
●
Where
clause
Aggregate functions
Aggregate
function perform set of values and returns single values as result
Sum
Add
column all values and return total of the column records
Min
Check
the column values and give minimum value
Max
Check
the column values and display maximum value
Avg
Add
all column values and divide no of values and give average of column
Count
Count
the number of elements in the column
Distinct
It
returns only different values
Order by function
Order
by function used to sort the values as ascending and descending orders
By
default order by function sort ascending order
Ascending order
Descending order
Group by function
Group
by function used to group the column value with specific condition
It can be used often aggregate
function
Having clause
Having
clause function added to sql because where class cannot be used in aggregate
function so we use having clause
Where clause
Where
clause is used to filter the records in the table
It
is used to retrieve records only full fill the condition
SQL joins
Join
clause is used to combine two are more tables,based on related column
between them
Types of joins;
INNER JOIN: Returns records that have matching
values in both tables
The
INNER JOIN keyword selects records that have matching values in both tables.
The
given example join two tables with their department number and display name dno
and hod name from studentdb and deptdb table
LEFT OUTER JOIN: Returns all records from the left
table, and the matched records from the right table
RIGHT
OUTER JOIN: Returns all records from the right table, and the matched records
from the left table
FULL OUTER
JOIN: Returns all records when there is a match in either left or right
table
SQL merge statement
Merge statement
Merge
command can perform multiple operation in single query
It
can be perform insert,update and delete operations.
The
MERGE statement basically merges data from a source result set to a target
table based on a condition
To
mention the source table and target table to perform merge operations
Target table source table
When matched
When not matched by target
When not matched by source
Insert ,update,delete
Syntax:
MERGE [AS TARGET]
USING [AS SOURCE]
ON
[WHEN MATCHED
THEN ]
[WHEN NOT MATCHED [BY TARGET]
THEN ]
[WHEN NOT MATCHED BY SOURCE
THEN ];
Merge
two table if records or matched it can be merged
If
records does not match
We
update the table record
Insert source table records to target table
Test
1 and 2 table create with 2 records only
Test
2 table add 2 more rows
Using
merge statement we merge test 1 and test 2 table
To
retrieve two table it can be a same data and tables are merged
Sql operators
Arithmetic operators
Character operator
Relational operators
Logical operators
Set operators
Arithmetic operators
●
Add-add
two column values
●
Subtract-subtract
two columns
●
Multiply-multiply
column values
●
Divide-divide
columns
●
Modulo-give
reminder values
Character operators
A wildcard character is used to
substitute one or more characters in a string
Like operators can be used
% -zero or more characters
-
single character
[] single character with brackets
-Range
of character
Relational operators
=
two values are equal
> a value grater b value
< a value less than b value
>= a value greater than equal
<= a value less than equal
<>
values not equal
Logical operators
And
Two where condition are true it give
result
Or
Any one condition satisfied it give
result
Not
Opposite result for given condition
Set operators
Union-The following statement combines the results of two
queries with the union operator
Intersect-
which
returns only those rows returned by both queries
Minus-
it returns only unique row in first query not second queries
SQL views
Views
View
is an virtual table, views contain rows and columns like real table. Create a
view with one or more tables
Simple view
Create view
Create a view name as department
from employee table.
Update view
Drop view;
Read only view
Only
read the view cannot be alter update
Complex views-
Complex
views can be created as multiple tables
Complex
views cannot be perform DML operations
Force view
A view can be
created even if the defining query of the view cannot be executed.
Desc views
Desc dba_views;
Desc
user_views
Grant
& revoke viws
Grant-give
permission to other user create view
Revoke-
get back the permission from given user
SQL synonyms;
Synonyms
●
Synonyms
provides another name of database object
●
Use
that name we can access the original database file
It can be create two parts
Local
or same database
Another
server
Creating a synonym within the same database;
Once
the orders synonym is created, we can reference it in anywhere which you use
the target object
Creating a synonym for a table in another database
Vijay
as other user room as table for vijay
user database ,vijay grant permission for create synonym for their table
So
we create synonym name as vikki3 to access vijay user room table
Other
user cannot give permission we cannot create synonym for other database
Grant & revoke synonym
We
give other database users can create synonym for table and also we get back
that permission to other users
Drop synonym;
Using
drop command we can delete the synonym
SQL sequences
Sequences
are set of integer values that can be generated to produced unique values in the database.
When
ever we need row as unique value we can use sequences statement.
Syntax
Sequence
name
Name
of the sequence
Initial
value
Starting
value of the sequence
Increment
value
Value
by which sequence will increment itself. it can be positive or negative.
Minimum
value
Minimum
value of the sequence
Maximum
value
Maximum
value of the sequence
Cycle
Sequence
reach limit its starts from beginning
Nocycle
Show
an error it reach maximum value
SQL Sub queries
Sub queries
Query
within another SQL query and embedded within the WHERE clause.
Sub
query can be used
select,update,insert,delete statements along with
>,<,>=,<=,in between operators
Subqueries with the SELECT Statement:
Select
the records in salary above 15000 by using sub queries we can retrieve the
records
Subqueries with the INSERT Statement
Insert
records with another table by using sub queries
Subqueries with the UPDATE Statement
Update
salary based on their age by using sub queries.
Subqueries with the DELETE Statement
Delete
records by using sql sub queries